In today’s data-driven world, organizations rely heavily on accurate, timely, and well-structured data to make informed decisions. Managing data from multiple sources, transforming it into a usable format, and storing it efficiently is a complex task. This is where SSIS 469 comes into focus. SSIS, or SQL Server Integration Services, is a powerful component of Microsoft SQL Server designed specifically for Extract, Transform, and Load (ETL) operations. It plays a critical role in modern data integration and business intelligence solutions.
SSIS 469 is often referenced in learning paths, certifications, or implementation contexts where mastering ETL concepts using SSIS is essential. Understanding how SSIS works and why it matters can significantly enhance data management capabilities for businesses of all sizes.
What Is SSIS?
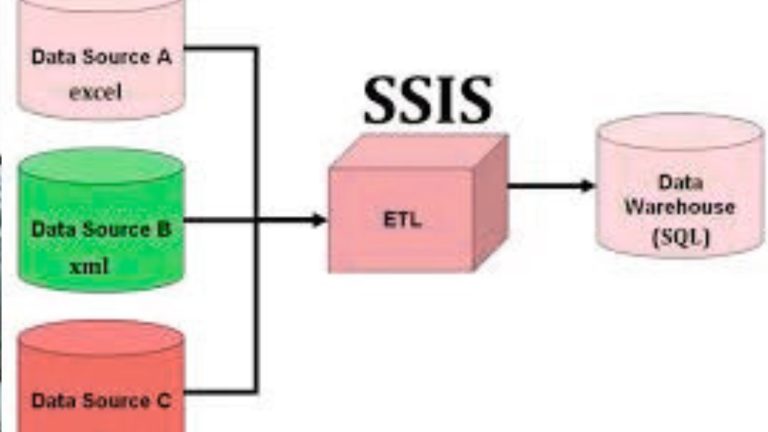
SQL Server Integration Services (SSIS) is a platform provided by Microsoft SQL Server that enables users to build high-performance data integration and data transformation solutions. It allows organizations to collect data from a wide range of sources, apply business rules or transformations, and load the processed data into a target system such as a data warehouse or reporting database.
SSIS is not just a data transfer tool. It is a comprehensive ETL framework that supports automation, scheduling, error handling, logging, and scalability.
Understanding SSIS 469
SSIS 469 typically refers to advanced usage or learning scenarios involving SSIS, where users work with complex ETL workflows, multiple data sources, and real-world business rules. It highlights the practical application of SSIS in enterprise environments where data accuracy and efficiency are critical.
At this level, SSIS is used not only for basic data movement but also for integrating diverse systems, cleaning data, and ensuring consistency across reporting platforms.
Extract: Gathering Data From Multiple Sources
The first step in any ETL process is extraction, and SSIS excels in this area.
Supported Data Sources
SSIS can extract data from a wide variety of sources, including:
- SQL Server databases
- Other relational databases
- Flat files such as CSV or text files
- Excel spreadsheets
- XML files
- Cloud-based and enterprise applications
This flexibility makes SSIS an ideal solution for organizations that rely on multiple systems to store operational data.
Efficient Data Extraction
SSIS uses optimized connectors and data flow components to ensure fast and reliable data extraction. It can handle large volumes of data while maintaining performance, which is essential for enterprise-level ETL operations.
Transform: Applying Business Rules to Data
Once data is extracted, it often needs to be cleaned, standardized, or reshaped before it can be used effectively. This is where the transformation phase becomes critical.
Data Cleansing and Validation
SSIS allows users to remove duplicates, correct invalid values, and apply validation rules. This ensures that the data loaded into the destination system is accurate and consistent.
Business Logic Implementation
Transformations in SSIS can reflect real business rules, such as:
- Calculating derived values
- Converting data types
- Merging data from multiple sources
- Splitting data based on conditions
These transformations help align raw data with business requirements, making it suitable for reporting and analysis.
Advanced Transformations
SSIS supports advanced transformations such as lookups, aggregations, and conditional logic. These features are especially useful in complex ETL scenarios often associated with SSIS 469-level implementations.
Load: Delivering Data to the Destination
The final step in the ETL process is loading the transformed data into a destination system.
Common Destinations
SSIS can load data into:
- Data warehouses
- Reporting databases
- Operational databases
- Cloud storage systems
This flexibility allows organizations to centralize their data for analytics, reporting, and decision-making.
Performance and Reliability
SSIS provides features such as bulk loading and transaction management to ensure that data is loaded efficiently and reliably. Error handling mechanisms help identify and resolve issues during the load process without compromising data integrity.
Key Features of SSIS
SSIS offers a rich set of features that make it a preferred ETL tool for many organizations.
Visual Development Environment
SSIS includes a user-friendly, graphical interface that allows developers to design ETL workflows using drag-and-drop components. This reduces development time and makes solutions easier to maintain.
Automation and Scheduling
SSIS packages can be scheduled to run automatically, enabling regular data updates without manual intervention. This is especially important for daily or real-time reporting systems.
Error Handling and Logging
Built-in error handling and logging features allow developers to monitor ETL processes, capture errors, and troubleshoot issues efficiently.
Scalability and Performance
SSIS is designed to handle large datasets and complex workflows. It can scale with business growth, making it suitable for both small projects and enterprise-level data integration.
Why SSIS 469 Matters for Businesses
SSIS 469-level knowledge is valuable because it focuses on real-world data challenges. Businesses generate massive amounts of data, and without proper ETL processes, this data becomes fragmented and unreliable.
By using SSIS effectively, organizations can:
- Improve data quality
- Reduce manual data processing
- Enable accurate reporting and analytics
- Support data-driven decision-making
SSIS ensures that the right data reaches the right systems at the right time.
Use Cases of SSIS in Real-World Scenarios
SSIS is widely used across industries for various purposes.
Data Warehousing
Organizations use SSIS to populate data warehouses with clean, structured data from multiple operational systems.
Reporting and Business Intelligence
SSIS feeds reporting databases that power dashboards, analytics tools, and executive reports.
System Integration
SSIS helps integrate legacy systems with modern platforms by transforming and migrating data seamlessly.
Conclusion
SSIS 469 represents a deeper understanding and application of SQL Server Integration Services in modern data environments. As a powerful ETL tool, SSIS enables organizations to extract data from diverse sources, transform it according to business rules, and load it into reliable destination systems. Its flexibility, performance, and scalability make it a cornerstone of data integration strategies.